Visual Flow Editor
The Visual Flow Editor lets you design complex multi-agent workflows using a node-based interface. Flows automate tasks by connecting triggers, agents, conditions, and actions into executable pipelines.
What is a Flow?
A Flow is an automated workflow that:
- Triggers based on events, schedules, or manual activation
- Executes one or more agents in sequence or parallel
- Processes data between steps with conditions and transformations
- Outputs results to tickets, files, or notifications
Flows enable powerful automation like:
- Daily research summaries
- Automated code reviews on PRs
- Multi-stage document processing
- Ticket triage and assignment
Flow Architecture
Flow Definition
interface Flow {
id: string; // Unique identifier (e.g., "flow-xxx")
name: string; // Display name
description: string; // What the flow does
nodes: FlowNodeData[]; // All nodes in the flow
edges: FlowEdge[]; // Connections between nodes
variables: Record<string, JSONSchema>; // Flow-level variables
labelIds: string[]; // Labels for organization
source?: 'user' | 'community'; // Origin of the flow
enabled?: boolean; // Whether automatic triggers are active
maxIterations?: number; // Max times a node can execute in loops (default: 5)
createdAt: Date;
updatedAt: Date;
}Flow Storage
Flows are persisted as JSON files:
- User flows:
.sciorex/flows/{flow-id}.json - Built-in flows:
resources/flows/(read-only)
Flow Editor Interface
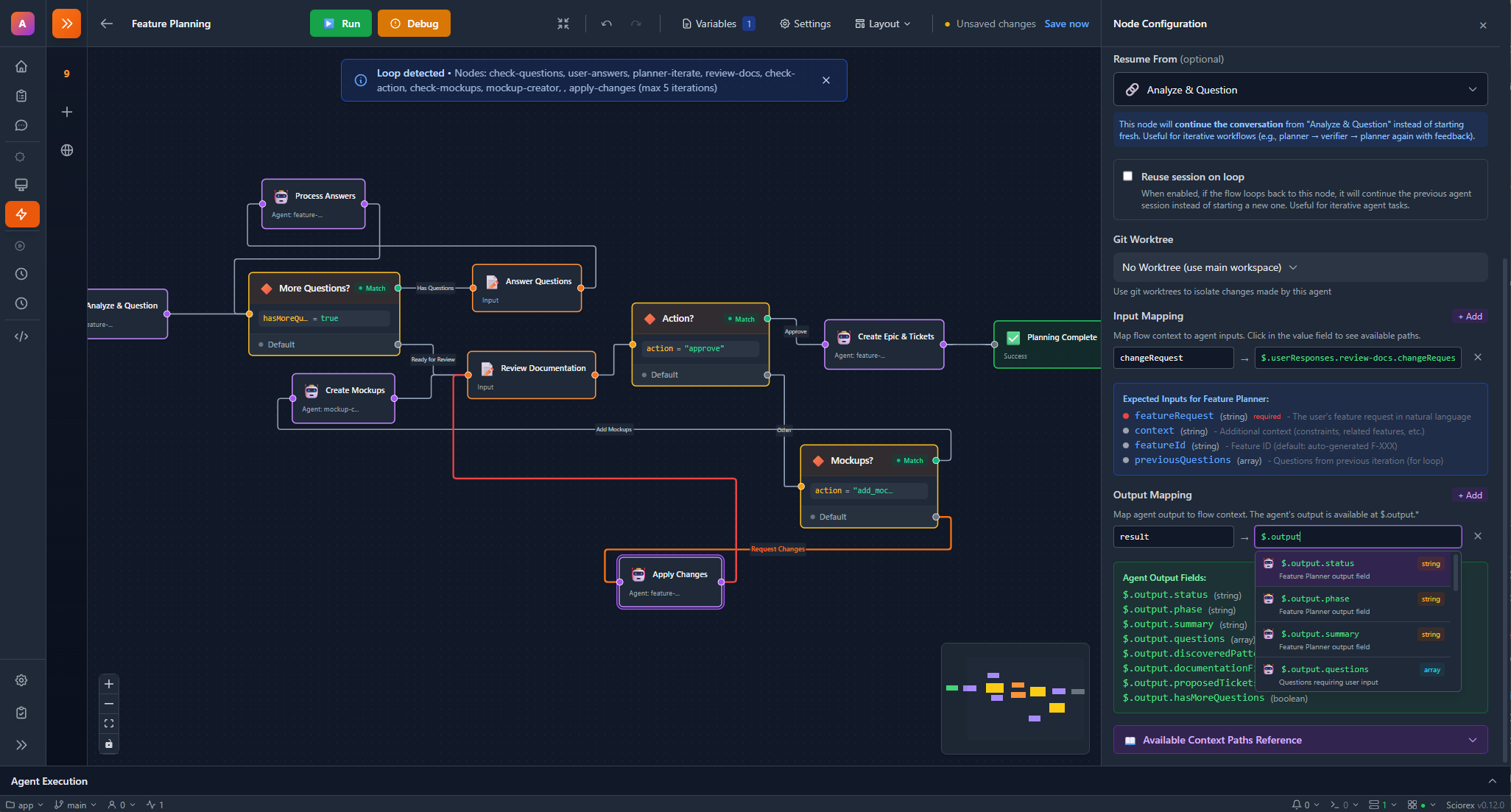
The editor provides:
- Canvas: Drag-and-drop node placement with zoom/pan
- Minimap: Overview navigation for large flows
- Sidebar: Node palette and property editor
- Toolbar: Save, run, validate, and execution controls
- Alignment Guides: Smart snapping for node alignment
Node Types
Trigger Node
Every flow starts with a trigger that initiates execution.
interface TriggerNodeData {
type: 'trigger';
triggerType: 'manual' | 'ticket-created' | 'ticket-updated' | 'schedule';
triggerConfig: {
cron?: string; // For schedule triggers
ticketFilter?: object; // For ticket triggers
inputSchema?: JSONSchema; // For manual triggers: defines expected input fields
};
}| Trigger Type | Description | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
manual | Run on-demand via UI or API | None required |
schedule | Cron-based scheduling | cron: "0 9 * * *" (daily at 9am) |
ticket-created | When a ticket is created | Optional ticket filter |
ticket-updated | When a ticket is updated | Optional ticket filter |
Agent Node
Executes an AI agent with input/output mapping.
interface AgentNodeData {
type: 'agent';
agentId: string;
inputMapping: Record<string, string>; // Map context to input
outputMapping: Record<string, string>; // Map output to context
outputSchema?: JSONSchema; // Override agent's output schema
worktreeMode?: 'none' | 'new' | 'inherit'; // Git worktree isolation
inheritWorktreeFromNodeId?: string; // Node to inherit worktree from
worktreeConfig?: { // Config for 'new' worktree mode
label?: string;
baseBranch?: string;
autoMergeOnSuccess?: boolean;
cleanupOnComplete?: boolean;
};
resumeFromNodeId?: string; // Resume a previous session
reuseSessionOnLoop?: boolean; // Reuse session in loop iterations
}Input Mapping Examples:
{
"query": "$.trigger.searchTerm",
"context": "$.nodes.previousAgent.output"
}Output Mapping Examples:
{
"$.results": "summary",
"$.metadata.sources": "sources"
}Condition Node
Routes execution based on context data evaluation.
interface ConditionNodeData {
type: 'condition';
conditions: FlowCondition[];
logicOperator: 'and' | 'or' | 'xor'; // How to combine conditions
negate?: boolean; // Invert the result (for NAND/NOR/XNOR logic)
targetNodeId?: string; // Node to go to when conditions match
defaultTargetNodeId?: string; // Node to go to when conditions don't match
}
interface FlowCondition {
path: string; // JSONPath to value (e.g., "$.results.score")
operator: string; // eq, ne, gt, lt, gte, lte, contains, matches
value: unknown; // Value to compare against
}Operators:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
eq | Equals | score eq 100 |
ne / neq | Not equals | status ne "failed" |
gt | Greater than | count gt 5 |
gte | Greater or equal | priority gte 3 |
lt | Less than | age lt 30 |
lte | Less or equal | version lte 2 |
contains | String contains | title contains "urgent" |
matches | Regex match | email matches ".*@company.com" |
Conditions evaluate to:
- Match edge: Follows when conditions are true
- Default edge: Follows when conditions are false
Wait Node
Pauses execution for human input or approval.
interface WaitNodeData {
type: 'wait';
waitType: 'approval' | 'input' | 'timeout';
prompt?: string; // Message to display
timeoutMs?: number; // Auto-continue timeout
inputSchema?: JSONSchema; // Schema for input collection
}| Wait Type | Description |
|---|---|
approval | Pause until user approves/rejects |
input | Pause until user provides input |
timeout | Pause for specified duration |
Parallel Node
Splits execution into multiple concurrent branches.
interface ParallelNodeData {
type: 'parallel';
branches: string[]; // Node IDs to execute in parallel
}Merge Node
Joins parallel branches back together.
interface MergeNodeData {
type: 'merge';
mergeStrategy: 'all' | 'any' | 'first';
sourceNodes: string[]; // Node IDs to wait for
}| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
all | Wait for all branches to complete |
any | Continue when any branch completes |
first | Continue when first branch completes |
Transform Node
Transforms data in the execution context.
interface TransformNodeData {
type: 'transform';
transformType: 'jq' | 'template' | 'script';
expression: string; // Transform expression
}| Transform | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
jq | JQ query syntax | .items | map(.name) |
template | Template string | {{nodes.agent.output.summary}} |
script | JavaScript code | return data.map(x => x * 2) |
Ticket Action Node
Performs actions on tickets.
interface TicketActionNodeData {
type: 'ticket_action';
action: 'create' | 'update_status' | 'add_comment' | 'add_label' | 'link_resource' | 'unlink_resource' | 'link_current_flow_run';
actionParams: Record<string, unknown>;
}End Node
Marks the end of a flow execution path.
interface EndNodeData {
type: 'end';
endType?: 'success' | 'failure' | 'cancelled';
}Flow Edges
Edges connect nodes and define execution order:
interface FlowEdge {
id: string;
source: string; // Source node ID
target: string; // Target node ID
sourceHandle?: string; // Output handle (for conditions)
targetHandle?: string; // Input handle
label?: string; // Edge label
}For condition nodes, edges use handles:
match- Condition is truedefault- Condition is false
Flow Execution
Execution States
enum FlowExecutionStatus {
Pending = 'pending',
Running = 'running',
Paused = 'paused',
Completed = 'completed',
Failed = 'failed',
Cancelled = 'cancelled',
}
enum NodeExecutionStatus {
Pending = 'pending',
Running = 'running',
Completed = 'completed',
Failed = 'failed',
Skipped = 'skipped',
Waiting = 'waiting',
}Execution Context
Each execution maintains a shared context:
interface FlowExecution {
id: string;
flowId: string;
status: FlowExecutionStatus;
context: Record<string, unknown>; // Shared data
nodeResults: Map<string, NodeExecutionResult>;
currentNodeIds: string[]; // Currently executing
nodeExecutionCounts: Record<string, number>; // Loop iteration tracking
output?: unknown; // Final flow output
archived?: boolean; // Whether the execution is archived
pausedAt?: Date; // When execution was paused
startedAt: Date;
completedAt?: Date;
error?: string;
}Context Paths
Access data using JSONPath-like syntax:
// Trigger input
{{trigger.input}}
{{$.trigger.searchQuery}}
// Previous node output
{{previousNode.output}}
// Specific node output
{{nodes.paperFinder.output}}
{{$.nodes.summarizer.output.summary}}
// Flow metadata
{{$.flowMeta.flowId}}
{{$.flowMeta.flowName}}Execution Algorithm
The flow executor uses topological ordering:
- Start: Create execution context from trigger
- Find Ready Nodes: Nodes whose dependencies are complete
- Execute in Parallel: Run ready nodes concurrently
- Update Context: Store node outputs
- Repeat: Until all paths reach end nodes
async executeFlow(executionId: string): Promise<void> {
while (true) {
// Check cancellation/pause
if (state.cancelRequested) return handleCancellation();
if (state.pauseRequested) return handlePause();
// Find and execute ready nodes
const executableNodes = findExecutableNodes(state);
if (executableNodes.length === 0 && runningNodes.size === 0) {
return isFlowComplete(state) ? handleCompletion() : handleStuck();
}
// Execute nodes in parallel
await Promise.race(executableNodes.map(nodeId => executeNode(state, nodeId)));
}
}Creating a Flow
Step 1: Add a Trigger
- Open the Flow Editor
- Drag a Trigger node onto the canvas
- Configure the trigger type and settings
Step 2: Add Processing Nodes
Connect nodes to build your workflow:
- Drag nodes from the sidebar
- Connect nodes by dragging from output to input handles
- Configure each node's properties
Step 3: Configure Data Flow
Use template expressions to pass data:
// Reference trigger input
{{trigger.input}}
// Reference previous node output
{{previousNode.output}}
// Reference specific node by name
{{nodes.paperFinder.output}}
// Extract specific fields
{{nodes.summarizer.output.summary}}Step 4: Save and Run
- Click Save to store the flow
- Click Run for manual execution
- View execution status in real-time
Flow Controls
During execution, you can:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Pause | Pause at next safe point |
| Resume | Continue paused execution |
| Cancel | Stop execution entirely |
| Inject Data | Provide input to waiting nodes |
Example Flows
Research Pipeline
Trigger (Daily @ 9am)
↓
Paper Finder Agent
↓
Summarizer Agent
↓
Create Ticket (sciorex_create_ticket)Use Case: Daily digest of new research papers
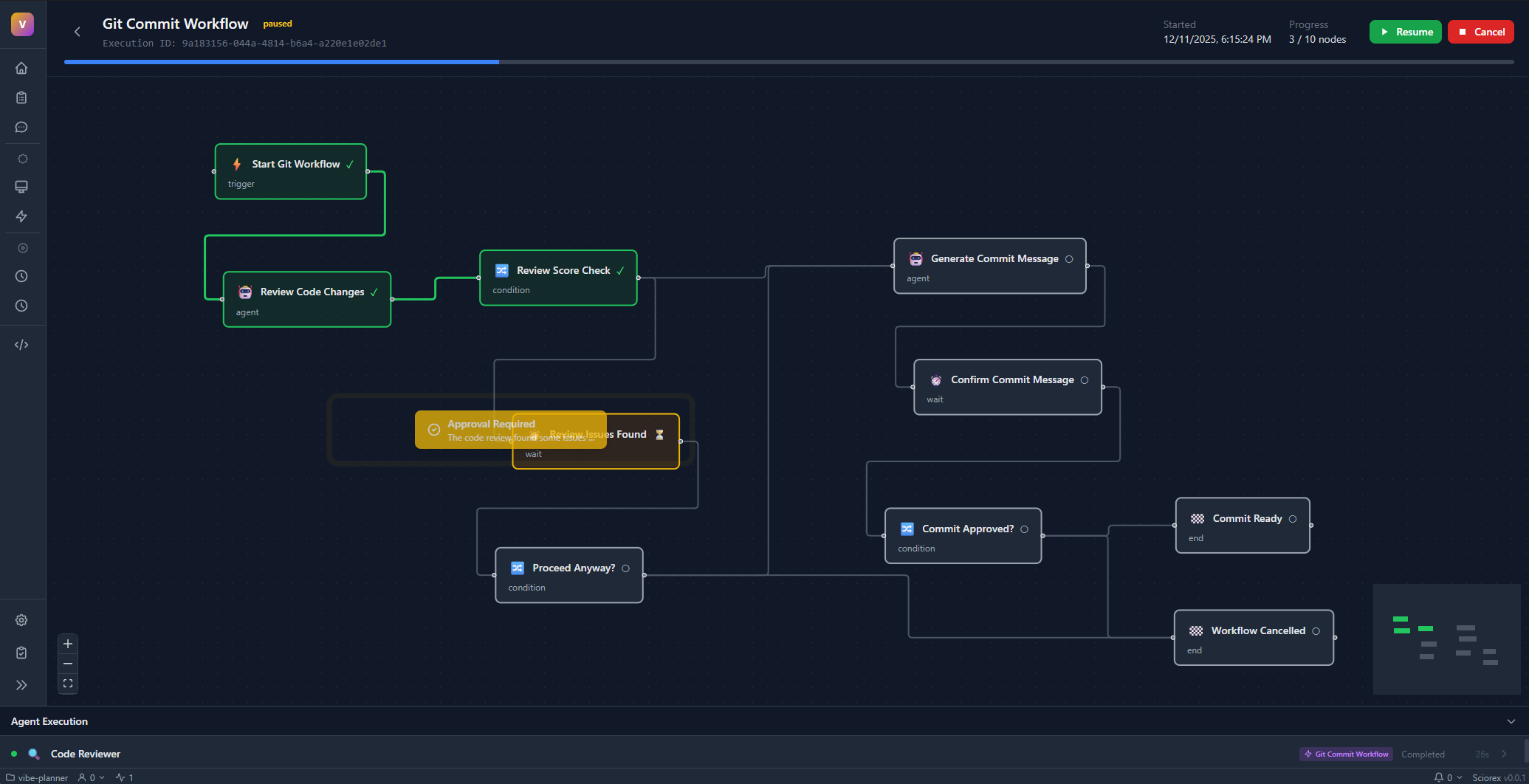
Code Review with Approval
Trigger (ticket-created, labels: "review")
↓
Code Analyzer Agent
↓
Security Scanner Agent
↓
Wait (Human Approval)
↓
┌─────┴─────┐
↓ ↓
Approve Reject
↓ ↓
Merge PR Request ChangesUse Case: Automated code review with human oversight
Parallel Processing
Trigger (Manual)
↓
┌───────────────────┐
│ Parallel │
│ ┌─────┐ ┌─────┐ │
│ │ A1 │ │ A2 │ │
│ └─────┘ └─────┘ │
└───────────────────┘
↓
Merge (strategy: all)
↓
Combine Results
↓
OutputUse Case: Process data with multiple agents concurrently
Conditional Routing
Trigger (ticket-updated)
↓
Triage Agent
↓
Condition (priority > 3)
├─ match → Urgent Handler Agent
└─ default → Standard Handler Agent
↓
Update Ticket StatusUse Case: Route tickets based on priority
Flow Validation
Flows are validated before execution:
| Check | Description |
|---|---|
| Has Trigger | At least one trigger node required |
| No Orphans | All nodes must be connected |
| Unique IDs | Node IDs must be unique |
| Valid Edges | Edges must reference existing nodes |
| No Cycles | Cycles trigger a warning (feedback loops must be intentional) |
| Valid Agents | Agent nodes must reference existing agents |
Flow Events
The flow engine emits events for monitoring:
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
flow:started | Flow execution began |
flow:completed | Flow finished successfully |
flow:failed | Flow ended with error |
flow:paused | Flow paused |
flow:resumed | Flow resumed |
node:started | Node began executing |
node:completed | Node finished successfully |
node:failed | Node ended with error |
node:waiting | Node waiting for input |
Debug Mode
Debug Mode lets you step through a flow node by node to inspect and modify data at each stage.
Debug Actions
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Step | Execute the next node and pause |
| Continue | Run until the next breakpoint or completion |
| Stop | Cancel the execution |
| Skip | Skip a node and provide mock output |
| Modify Input | Change a node's resolved inputs before execution |
| Modify Output | Change a node's output after execution |
Breakpoints
Set breakpoints on nodes to pause execution at specific points. Breakpoints can trigger before or after node execution, letting you inspect resolved inputs and actual outputs.
interface DebugBreakpoint {
nodeId: string;
type: 'before' | 'after';
}Error Recovery
When a node fails during execution (outside Debug Mode), the flow pauses and presents recovery options:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Retry | Re-execute the failed node |
| Skip | Skip the node and provide mock output to continue the flow |
| Stop | Cancel the entire execution |
interface NodeErrorState {
nodeId: string;
error: string;
timestamp: Date;
recoveryAction?: 'skip' | 'retry' | 'stop';
mockOutput?: unknown; // Used when skipping a failed node
}Worktree Isolation
Agent nodes can run in isolated Git worktrees, keeping changes separate from the main branch:
| Worktree Mode | Description |
|---|---|
none | No worktree (default) |
new | Create a new worktree for this node |
inherit | Reuse a worktree from another node |
When using new mode, you can configure:
- Base branch for the worktree
- Auto-merge on success to merge changes back automatically
- Cleanup on complete to remove the worktree after use
Use inherit with inheritWorktreeFromNodeId to share a worktree between sequential nodes (e.g., Plan → Implement → Review all working on the same branch).
Best Practices
Start simple
Begin with linear flows before adding conditions and parallelism.
Use descriptive names
Name your nodes clearly (e.g., "Summarize Papers" not "Agent 1").
Handle errors
Add error handling nodes for critical workflows. Consider using condition nodes to check for errors.
Test incrementally
Run flows after adding each node to catch issues early.
Avoid infinite loops
Be careful with cycles - ensure they have proper exit conditions.
Integration with Tickets
Flows integrate deeply with the ticketing system:
- Trigger on ticket events: Start flows when tickets are created/updated
- Create tickets from flows: Use Ticket Action nodes
- Update ticket status: Modify tickets during execution
- Link sessions: Flow agent sessions can be linked to tickets
API Operations
Create Flow
const flow = await flowService.createFlow({
name: 'My Workflow',
description: 'Automated pipeline',
nodes: [...],
edges: [...]
});Execute Flow
const execution = await flowExecutor.startFlow(flow, {
searchQuery: 'machine learning' // Initial context
});Control Execution
flowExecutor.pauseExecution(executionId);
flowExecutor.resumeExecution(executionId);
flowExecutor.cancelExecution(executionId);Inject Data
await flowExecutor.injectData(executionId, nodeId, {
userInput: 'approved'
});Next Steps
- AI Agents - Configure agents for flows
- MCP Servers - Extend flow capabilities
- Ticketing System - Integrate with tickets
- AI Backend - How agents execute
