Understanding Workflows (Flows)
Flows let you chain agents together into automated pipelines. Instead of manually running each step, you define the sequence once and let it run on its own.
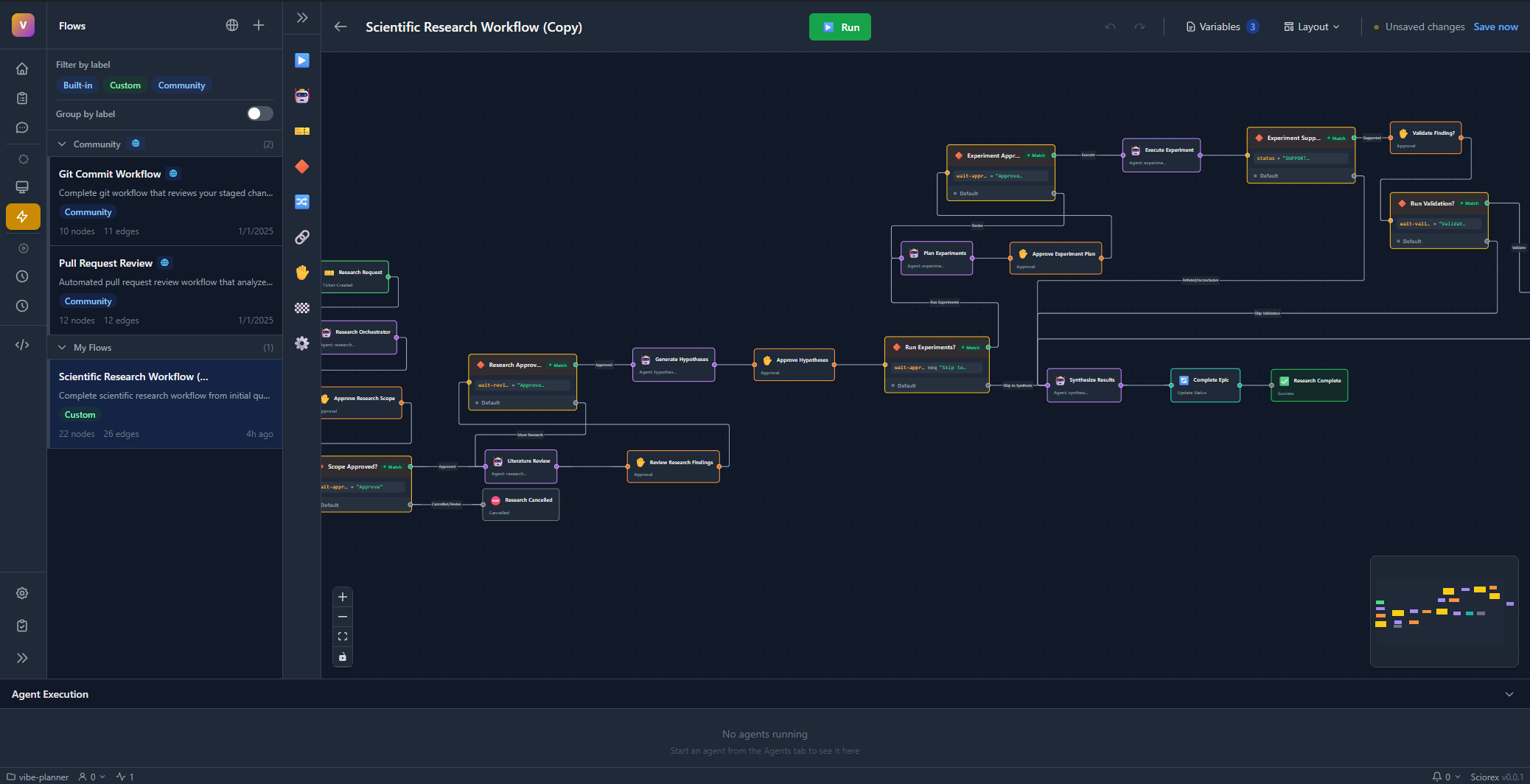
What is a Flow?
A flow is a visual diagram that defines:
- When to start (trigger)
- What to do (agents and actions)
- How to decide (conditions)
- Where to go next (connections)
Common Use Cases
| Flow Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Research Pipeline | Find papers Summarize Create ticket |
| Code Review | Analyze code Check security Wait for approval Merge |
| Data Processing | Fetch data Clean Analyze Generate report |
| Ticket Automation | New ticket Triage Assign Notify team |
| Research Automation | Search papers Annotate PDFs Update references Create summary |
Building Blocks
Triggers
Every flow starts with a trigger:
| Trigger | When it fires |
|---|---|
| Manual | You click "Run" (supports inputSchema for defining expected input fields) |
| Schedule | At specific times using cron expressions |
| Ticket Created | When a new ticket is created (with optional ticket filter) |
| Ticket Updated | When a ticket changes (with optional ticket filter) |
Nodes
Nodes are the steps in your flow:
| Node Type | What it does |
|---|---|
| Agent | Runs an AI agent with input/output mapping and optional worktree isolation |
| Condition | Routes based on conditions using JSONPath, operators (eq, ne, gt, lt, contains, matches), and logic (AND/OR/XOR with optional negation) |
| Wait | Pauses for human approval, user input, or a timeout |
| Parallel | Splits into multiple concurrent branches |
| Merge | Joins branches with strategy: wait for all, any, or first |
| Ticket Action | Creates, updates, comments, labels, or links resources on tickets |
| Transform | Modifies data using jq queries, templates, or scripts |
| End | Marks the end of an execution path (success, failure, or cancelled) |
Connections
Lines between nodes show the execution order. For condition nodes, you'll have two paths: one for "yes" and one for "no".
Creating Your First Flow
- Go to Flows in the sidebar
- Click New Flow
- Drag a Trigger node onto the canvas
- Drag an Agent node and connect it
- Configure each node's settings
- Click Save
- Click Run to test
Passing Data Between Nodes
Agent nodes use input mapping and output mapping to pass data through a shared execution context:
inputMappingmaps agent input schema fields to context paths (e.g.,{ "topic": "trigger.input.topic" })outputMappingmaps agent output schema fields back to context paths (e.g.,{ "summary": "nodes.summarizer.output" })
The execution context is a shared data store that all nodes read from and write to as the flow progresses.
Controlling Execution
Flow execution status progresses through: Pending, Running, Paused, Completed, Failed, or Cancelled.
While a flow runs, you can:
- Pause it to inspect progress
- Resume after pausing
- Cancel to stop entirely
- Inject data when a Wait node needs input
Debug Mode
Enable Debug Mode to step through your flow node by node:
- Step — execute the next node and pause
- Continue — run until the next breakpoint or completion
- Stop — cancel the execution
- Skip — skip a node and provide mock output
- Modify Input — change a node's resolved inputs before it runs
- Modify Output — change a node's output after it runs
Debug Mode shows resolved inputs, expected next nodes, and actual output at each breakpoint (before or after node execution).
Error Recovery
When a node fails during execution (outside Debug Mode), the flow pauses and presents recovery options:
- Retry — re-execute the failed node
- Skip — skip the node and provide mock output to continue the flow
- Stop — cancel the entire execution
Best Practices
Start simple. Build a linear flow first, then add conditions and parallelism.
Name nodes clearly. "Summarize Papers" is better than "Agent 1".
Test incrementally. Run after adding each node to catch problems early.
Handle errors. Use error recovery to retry or skip failed nodes, or add condition nodes to check for failures.
Use worktrees for isolation. Agent nodes support worktree mode (none, new, or inherit) to give each agent its own Git worktree. New worktrees can auto-merge on success and clean up on completion. Use inherit to share a worktree between nodes.
Use labels. Organize flows with labels for easy filtering and discovery.
Avoid infinite loops
If you create cycles in your flow, set the maxIterations property (default: 5) to limit how many times a node can execute in a loop.
Next Steps
- Research Pipeline - Build a multi-agent flow
- Research Suite - Use research tools in automated flows
- Flow Editor reference
- Node types in detail
- Example flows
